The diagnosis is the first step to feeling better. Once you know, there are several home remedies and over-the-counter (OTC) medications you can try to help relieve symptoms and feel better while your body works to fight off infection. Oh, and a bowl of chicken soup can’t hurt, either. It is very important to remember if you have a cold, flu, or other non-bacterial illness, you should not ask your doctor for antibiotics (such as a “Z-Pak”), as these medications cannot treat a viral infection.
Here’s how to tell the difference between a cold, flu, and sinus infection:
You Have: A Cold
What it is: A respiratory illness caused by a virus. Many types of viruses can cause a common cold, but rhinoviruses are the most common culprit.
Common Symptoms: Cold symptoms usually develop pretty gradually over one to three days and are generally considered to be more mild. Signs and symptoms1
Runny or stuffy nose, sneezing
Sore throat, cough
Congestion
Mild body aches or headache
Low-grade fever (this is not as common)
Overall tiredness and fatigue
How to Treat it: As you’ve probably heard, there’s no cure for the common cold. It’s unfortunate, we know! Instead, you can take care of your body by drinking lots of water, eating healthy, and resting. You can also take OTC medicines to help treat some of the nasty symptoms you’re experiencing. Symptoms can last for about a week, according to Harvard Medical School2 .
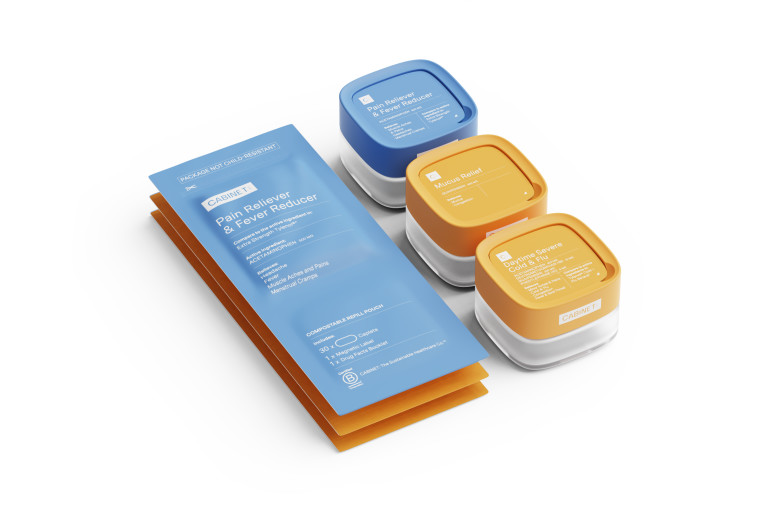
If you’re looking to relieve symptoms (and help the planet) Cabinet can help with:
Nasal congestion and sinus pressure - Nasal Decongestant (phenylephrine)
Frequent cough
Fever and aches - Pain Reliever & Fever Reducer (acetaminophen)
Overall relief from common cold symptoms, including fever - Daytime Severe Cold & Flu
Note: In general, medicines with only one active ingredient can be combined. If you’re taking a cold medicine that offers multi-symptom relief, like Daytime Severe Cold & Flu, avoid combining it with other medicines. This is because combination pills often have the same ingredients in them and taking too much is not safe. Check with a pharmacist before combining any cold medicines
You Have: The Flu (Influenza)
What it is: A respiratory illness caused by a virus that can have serious complications, such as pneumonia. The flu is caused by influenza viruses. These viruses mutate and evolve very quickly.
Common Symptoms: Unlike cold symptoms, flu symptoms develop more quickly and are generally more severe. You know you have the flu if symptoms seem to hit you like a truck. Signs and symptoms3 of the flu may include:
Fever
Muscle aches, headaches
Chills and cold sweats
Persistent cough that are usually dry, sore throat
Shortness of breath
General fatigue and feeling weak
Stuffy or runny nose
Diarrhea and vomiting (more common in children)
How to Treat it: Generally, the flu is managed the same way as a cold—with fluids, rest, and OTC options for symptom relief. Most people can grab a Cold & Flu Bundle, bundle up in bed with some soup, and rest. Symptoms generally last for about a week, but can last longer in some people. People who’ve received a flu shot may experience less severe symptoms or symptoms that last a shorter amount of time.
If you have a severe influenza infection or are considered high risk for complications (i.e. elderly, weakened immune system, chronic illnesses, pregnancy), your doctor may prescribe an antiviral medication, such as oseltamivir (Tamiflu)4 to treat the flu. Antiviral medications are most effective if taken within 48 hours of symptom onset and can shorten the duration of the flu (usually by a day or two). They can also prevent serious complications from arising, such as pneumonia, bronchitis, and heart problems.
Prevention Tips: The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends the annual flu shot for everyone age 6 months or older5 . The flu vaccine can reduce: the risk of getting the flu, the severity of symptoms, and the risk of serious complications from the virus. Flu season typically runs from the start of fall to the end of spring, so make sure to get your flu vaccine annually! Since these pesky flu viruses evolve so quickly, new flu vaccines must be created each year to keep up and better protect you from them.
The flu vaccine isn’t 100% effective, so we must also take steps to prevent the spread of infection. Please refer to the prevention tips in the cold section for best practice recommendations.
You Have: A Sinus Infection (Sinusitis)
What it is: Inflammation of the tissue that lines the sinus cavities most often caused by the common cold, allergies, or nasal polyps.
Want more details? The sinuses produce mucus, which is a thin liquid used to moisten the nose and protect against germs, allergens and other foreign irritants. Sometimes, your sinuses can become blocked and filled with unwanted germs or bacteria, causing an infection6 .
Common Symptoms: Just like a cold, you may experience a runny or stuffy nose, sore throat, and cough. Other symptoms of a sinus infection may include:
Thick, yellow or green mucus in the nose or throat
Facial pain and pressure that feels worse when bending over
Ear pressure, headache
Aching in your teeth
Altered sense of smell
Bad breath
Fatigue
Fever
How to Treat it: In addition to getting plenty of rest and liquids, some other options for treatment or symptom relief include:
Applying a warm compress over your sinuses
Taking steamy showers
Saline nasal spray. These sprays can be used to rinse out your nasal passages.
Nasal corticosteroids. Corticosteroid sprays and mists, such as fluticasone (Flonase Allergy Relief) and budesonide (Rhinocort Allergy), target swelling, inflammation, and congestion in the nasal passages.
OTC decongestants. Oral and nasal decongestants can be very effective for congestion relief, such as Nasal Decongestant. Learn more about congestion and the use of nasal decongestants here.
Allergy medications. Antihistamines, such as Allergy Relief, may be helpful for sinusitis caused by allergies.
OTC pain relievers. Pain relievers, like Pain & Fever Relief or ibuprofen (Advil), can be used to relieve fever, aches, and pains.
Antibiotics. If your sinus infection is caused by bacteria, your doctor may prescribe you antibiotics. Be skeptical if your provider automatically offers you an antibiotic without first checking to see if you have a viral or bacterial infection.
Prevention Tips: Here are some steps7 you can take to help prevent getting a sinus infection:
Stay away from people who have colds or other upper respiratory infections
Wash your hands frequently with soap and water. Sanitize your hands often.
Keep your allergies under control. If you have allergy symptoms that just won’t go away, work with your healthcare provider to develop a treatment plan.
Avoid irritants like smoke and polluted air
Try using a humidifier and avoiding dry environments to help prevent your nasal passages from drying out